Every day, $5.1 trillion is transacted in the Forex market. This is the largest financial market, dwarfing even the largest stock exchanges like the NYSE averaging about $77 billion on the 31st of May 2018. Not only does the large figure mean that there are a lot of opportunities in the market, but it also means rigging is very difficult, even for the largest and most influential participants. This is why it is so unusual to hear that there has been a major currency fixing scandal that led to about $8 billion in fines by those involved. 14 major investment banks offering Forex trading have been caught in the racket, which should have your eyebrows raised. All Forex traders should be aware of how such scandals are run if we are going to have a better understanding of the markets. (Here are the: Top 10 Most Outrageous Forex Market Scammers)
How do major investment banks manipulate Forex markets?
Among all the participants in the Forex market, the major players are investment banks, private equity firms, hedge funds, multinational corporations, and central banks. Being extremely liquid, they transact billions in transactions, raising the daily traded volume 24/5. Nevertheless, even the largest hedge fund or bank cannot manipulate a $5.1 trillion market alone, so they have come up with ingenious ways to do it. The most common and widely used trick is employed during the London 4 pm fix. (Lessons on self-defense: Forex scams)
What is the London 4 pm fix?
Although the Forex markets are usually advertised to run constantly for 5 days a week, the truth is not so simple. Have you ever wondered how overnight swaps are calculated by your bank, this should be a clue. At the end of the day, your Forex broker simultaneously closes your position at the current market prices and then purchases futures for the currency pair to ensure they get the price they desire. In the process, you may receive a positive or negative swap depending on the interest rates of each country’s currency. (Find out: What Is The Financial Commission And Can It Be Trusted?)
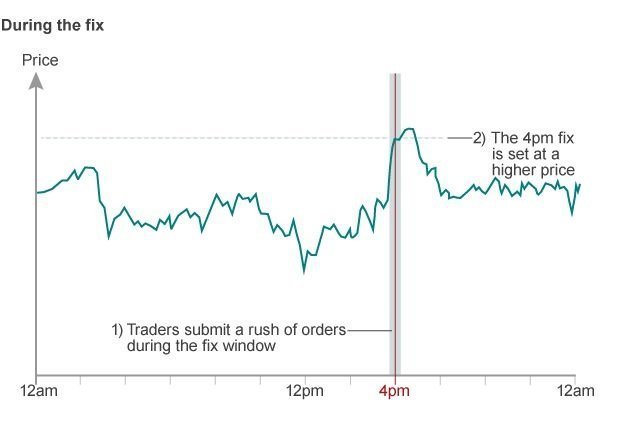
This isn’t the only adjustment made over the 5 days when the markets are open, as there is also a ‘fix’ made at 4 pm every day, London time. 30 seconds before and 30 seconds after 4 pm, an average of the exchange rates for major currency pairs is taken. This average is then used to create an average for the rest of the currency pairs. The 4 pm fix was created in 1994 and is run by WM Company as well as Reuters to ensure there is some regularity within the markets. Since the Forex market is decentralized, the average got from the 4 pm fix attempts to regulate the entire market. (All you need to know, the: Basics of stock trading)
Some very creative currency traders saw this as an opportunity to profit by manipulating the market and did so very profitably. Of course, even a billion-dollar AUM hedge fund cannot drastically change the market quotes, but that is all they need. Consider an example where the EUR/USD pair currently trading at 1.16400 was made to shift just a few pips to 1.16450. That 50-pip movement may be negligible for an individual trader whose trade translates to about $1 per pip, but for a major bank where every pip represents $100,000… well, you do the math. (Have you ever wondered: Should You Invest In CFDs Or Stocks To Make More Money?)
The London 4 pm fix had been around since 1994, but it was modified in February 2015 after investigations by Bloomberg News showed how some traders were taking advantage of it. Many trusted Forex market regulators had been investigating the fix, and they decided to lengthen the period required for the fix. Instead of 30 seconds before and after 4 pm, the time required is now 5 minutes before and after 4 pm, which is a lot harder to manipulate. (These are the: 10 rules of how to earn money with scalping)
What is gained from fixing currency rates?
An example of the fix can happen as such – WM Company takes an average of the major currency pairs, let’s assume the GBP/USD pair could be trading at 1.31505 30 seconds before 4 pm. Within the one minute before the second average is taken 30 seconds after 4 pm, a trader at an investment bank could place a huge order into the market that causes a sharp spike or dip in prices. Such a trade would benefit the bank in two ways. First, the sharp spike in prices would be a profit for the investment firm since the change in prices causes a difference between the buying and selling price for example, in our above example, had the EUR/USD pair risen from 1.16400 to 1.16450 with every pip worth $100,000, then that would be a $5 million profit on a single trade. (DO you know exactly: How Is Spread Betting Different From Forex Trading?)
Secondly, the sharp spike in prices would increase the spreads and subsequently raise the cost to their clients. The most popular Forex ECN brokers use investment banks as their liquidity providers. They receive the market quotes as the bid/ask prices, with the difference being the spread and the profit to the liquidity provider. During the fix, the liquidity provider would thus increase the spread and earn more from their clients as a result. They can do this because, as liquidity providers, they know how their clients are placing their trades and can use this information to their advantage. Assuming a trader got a huge order to buy a certain currency pair before the fix, they could use this to manipulate the prices and charge the client a lot more. (All successful traders know: How to find the best Forex spreads)
Who are some of those involved?
Although the total compensation by the culprits was around $8 billion, it is thought that a lot more was lost through this currency manipulation scheme. Considering that the culprits had been doing these kinds of activities starting from 2003 to 2015, it is likely true that there was more loot. Following these findings, all the affected companies have the right to claim any money they lost, which was the intended purpose of the fines. All in all, this may have been one of the most prolific financial scandals yet due to its magnitude. (Which is better: Long-term vs. short-term trading)
Among those banks found to have attempted the 4 pm London fix include JP Morgan Chase, Citigroup, Barclays, Deutsche Bank, and other major names. In one case highlighted by BBC, HSBC made a $162,000 profit during the fix by lowering the GBP/USD exchange rate from £1.6044 to £1.6009. After combing the traders’ correspondence thereafter, the FCA discovered congratulatory messages among the traders themselves for ‘nice teamwork’. The most heavily fined bank in the currency fixing scandal was Barclays which had to pay $ 2.4 billion. Behind it was Citibank which was fined $310 million by the CFTC and $358 million by the FCA. The other major banks in the scandal were HSBC, JP Morgan, Royal Bank of Scotland (RBS), and UBS Group. (These are: The 3 Most Trusted Exchange Authorities in The World)
Colluding to change currency rates
Through investigations by financial regulators, they found some exclusive chatrooms used by the traders to further manipulate the markets. Only the top traders in the above banks were invited to these chatrooms that had names such as ‘The Cartel’ and ‘The Mafia’. Through these chatrooms, traders would also collude to change the market quotes in their favor. Since a single trader cannot move the markets significantly, they would combine their collective resources and make a trade at a specified time. With the resources of the banks, they could be able to change the exchange rates of the major currency pairs in whatever direction they wanted. (How about we try: Comparing fundamental and technical analysis)
In other cases, the traders used their inside knowledge to profit from the expected price moves that are still not public. Such practices are known as front-running, and one of the most prominent cases involved HSBC. In 2016, two HSBC employees knew that one of their clients, Cairn Energy Plc. wanted to convert $3.5 billion to sterling pounds. Before making this transaction for Cairn, the traders began buying more pounds in anticipation of the spike in value. After the spike, they could then sell the pounds for a profit. (Do you know: What is carry trade?)
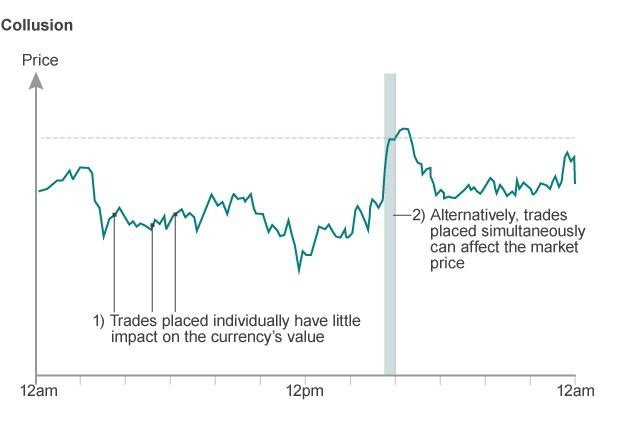
Many other traders did the same thing through the private chatrooms, revealing another way in which they rigged the markets in their favor. Just like the London 4 pm fix, collusion is also just as effective when timed right. Furthermore, these major bank traders would ask other traders from smaller banks to route their orders through them to increase the impact in the markets. (Do you know: How much money Forex brokers make?)
Who gets hurt from this and what can be done?
At first, it may seem like there wasn’t much harm done. Perhaps the manipulation of exchange rates by a few pips didn’t hurt anyone all that much, but it does affect the entire market as a whole. Through the investigations, a deeper rot was discovered by Bloomberg – that the Bank of England was aware of the fixing since as early as 2006. Instead of fixing the fix, they promoted it saying that it reduced market volatility. What this all reveals is that there is a need for more scrutiny in the Forex markets. Several proposals are being considered right now, including one to make the FX market centralized. However, these are still raw ideas with their different sets of challenges. In the meantime, the FX Global Code of Conduct is the only document that outlines some of the measures all market participants should adhere to. (These are the: Main central bank meetings)
Those who got hurt most, even though they didn’t know it at the time, were the Forex brokers and retail traders. Those affected are eligible for compensation from the fines collected. Although there is a lot of money on the line, many of those affected may still be wary of going through with the claims process. For one, the process of filing a claim is not straightforward. Mainly, the Forex market is not centralized meaning that there may be millions of transactions the broker Forex may have handled from 2003 to 2015. To prove that their market quotes need revision, they would have to detail all of these transactions through various Forex trading platforms. It is not an easy task, and many FX brokers may choose to eat the cost in the end.
There is an even more sinister reason why brokers may be reticent – the fear of compromising their relationships with the liquidity providers. Imagine an ECN broker who receives their quotes from a handful of banks acting as liquidity providers. If the bank finds out the broker is pursuing a claim, they may feel betrayed and seek to punish them by denying further services. For such a Forex company, this can be a major deterrent if they would like to keep running their business. After all, didn’t they transfer those same quotes to the clients? (You should try: Trading using central banks' reports)
To see some of the action in the video, here is a short clip taken from a news segment:

 RoboForex
RoboForex Exness
Exness FxPro
FxPro Alfa-Forex
Alfa-Forex Libertex
Libertex FxGlory
FxGlory XM
XM IC Markets
IC Markets Forex.com
Forex.com AXITrader
AXITrader