Have you ever been on the verge of a big win in the market, only to have it slip through your fingers? This can be frustrating and disheartening, especially when you feel like you have everything under control. But the reality is, even the most experienced traders can fall victim to psychological trading mistakes, such as overconfidence, revenge trading, and cognitive biases.
Imagine you're a chef, preparing a meal for a prestigious culinary competition. You've carefully selected the finest ingredients and have spent countless hours perfecting your recipe. But as you're about to plate your dish, you realize that you added salt instead of sugar to the dessert. This mistake could cost you the competition, just like psychological forex trading mistakes can cost traders their profits.
So, what are these psychological trading mistakes, and how do they cost traders their profits? How can you avoid them and ensure that your trading strategy stays on track?
In this article, we'll explore the most common psychological trading mistakes that you can make without knowing and the hidden costs they bring. Then, we'll provide practical strategies for avoiding these mistakes and reaching your financial goals. By recognizing and sidestepping these pitfalls, traders can minimize risk.
Here is how to make the right moves in the world of psychological trading!
5 Common Forex Trading Psychological Mistakes
Mistake 1: Revenge Trading
Revenge trading is just like the fear of missing out (FOMO) steam from two powerful emotions:
-
The desire to make money – is often driven by greed.
-
Being afraid to accept a trading loss – often driven by fear.
Revenge trading is the act of trying to recover from losing trades quickly. But this also leads to overtrading.
For example, consider a trader who has been consistently making profits but suddenly experiences a losing streak. Frustrated and determined to recoup their losses, the trader may impulsively increase their trade size or take on higher-risk trades without fully analyzing the market conditions.
The trader, who typically operates with 1 standard lot per trade, may be tempted to depart from their established comfort zone and amplify their volume by trading 2 or even 3 standard lots to recoup losses.
This hasty behavior can lead to further losses and put the trader in an even worse position than before.
How To Avoid Revenge Trading?
One may wonder, "How do I stop being addicted to trading?"
The answer is to remember that every trading decision should be based on some form of analysis, whether it be technical, fundamental, or price action.
This helps to prevent revenge trading and other forex psychological mistakes and ensures that each trade is made with a calculated and rational approach. Too much confidence in one's abilities can also be a hindrance and result in costly mistakes.
Mistake 2: The Fallacy Of Shifting Blame In Trading
The fallacy of externalizing blame in trading refers to the psychological mistake of attributing one's trading failures to external factors, rather than accepting personal responsibility for their decisions. This tendency to blame market conditions, forex brokers, or other external factors for losses can prevent traders from recognizing and addressing the root causes of their issues.
What Mindset Should A Trader Have?
A trader must adopt an introspective approach and acknowledge their role in each trade outcome. This includes accepting responsibility for the decisions they make and recognizing their own biases, emotions, and limitations as traders.
By accepting personal responsibility, traders can learn from their mistakes, make positive changes, and ultimately improve their trading performance.
Externalizing blame not only hinders personal growth and development as a trader but also reinforces negative behaviors and hinders progress. Instead of learning from mistakes and finding ways to improve, traders who externalize blame remain trapped in a cycle of repeating their errors and seeking excuses for their losses.
Mistake 3: Marrying A Trade Idea And Cognitive Biases
Cognitive bias shows up most obviously in traders' tendency to interpret information in a way that supports existing beliefs or ideas. This can lead traders to overlook important information and ignore market signals that do not align with their preconceived notions.
Attachment to a trade idea can result in traders holding on to a position for too long, even as it continues to incur losses.
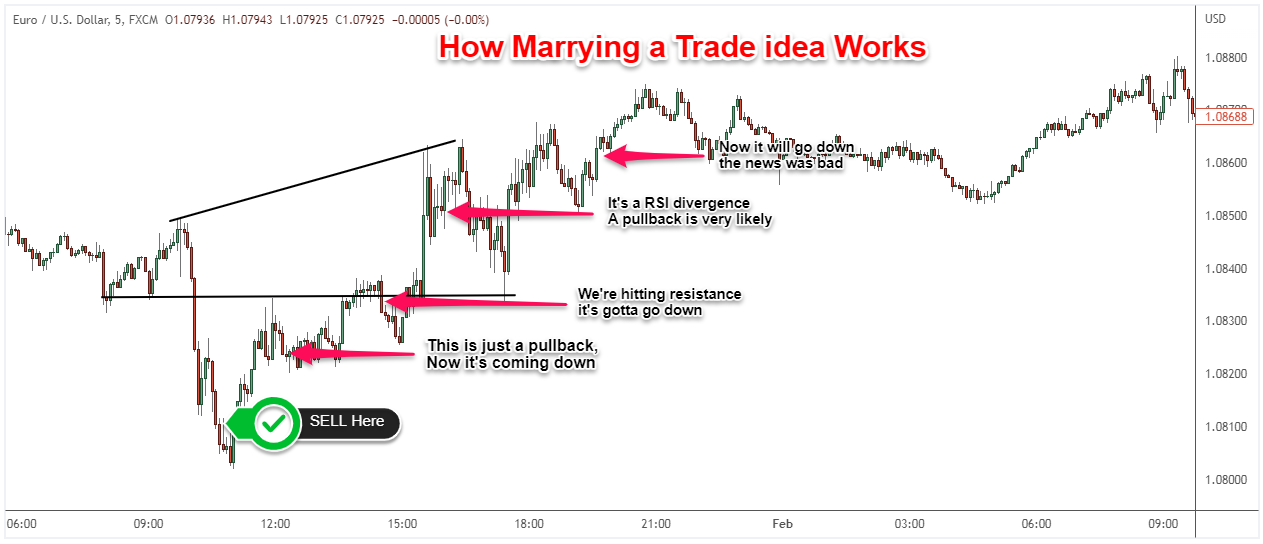
One of the reasons traders become "married" to trade is due to the sunk-cost bias. This refers to the psychological tendency to cling to a losing investment to justify the initial trade decision. In other words, traders may hold on to a losing trade to avoid admitting that they made a mistake and avoid realizing a loss.
Traders also become attached to a trade idea due to the false belief that the price will rebound in their favor. Most times, this mentality can cause traders to ignore real-time market signals and make decisions that lead to more losses.
How Do I Fix Cognitive Bias?
To avoid becoming "married" to a trade idea, traders should have a well-defined and rigid exit strategy in place. This means that you have the opportunity to minimize your losses by cutting them early and moving on to the next trade.
In trading, it's normal to be wrong from time to time. But it's crucial to avoid staying wrong and letting your emotions dictate your trading decisions.
Mistake 4: Gambler’s fallacy
The gambler's fallacy is a common psychological mistake in trading where a trader assumes that past outcomes of a random event, such as the movement of a currency pair, will influence future outcomes. This leads to the belief that a certain event is more likely to happen after a series of outcomes of the opposite event.
For example, a trader who has observed a string of losses in a particular currency pair may believe that a win is due, and as a result, increase their trade size or hold on to a losing position for too long, hoping for a turnaround. This fallacy can be dangerous as it ignores the fact that each trade is independent of the previous one and that past outcomes do not determine future outcomes.
Mistake 5: The Unrealistic Goal Or Trying To Make Every Trade A Home Run
When it comes to trading, it's easy to fall into the trap of wanting to make every trade a home run. The desire for big profits can be all-consuming, leading traders to overlook the importance of taking a more balanced and realistic approach. Opportunities for high-reward, low-risk trades are rare in the forex market. Trying to make every trade a home run can lead to unrealistic expectations and set traders up for disappointment.
Instead, it's crucial to keep things in perspective and strive for a balanced approach that involves a combination of fast small profits, slow big gains, and losses in between.
Final Thoughts
The main takeaway is that all traders are prone to psychological trading mistakes, but these should be treated as opportunities to grow as a trader. The aim should always be to admit it, learn from it, and never repeat the same mistake.
Start your path to better trading and avoid costly mistakes by visiting the top Forex brokers page now.

 RoboForex
RoboForex Exness
Exness FxPro
FxPro Alfa-Forex
Alfa-Forex Libertex
Libertex FxGlory
FxGlory XM
XM IC Markets
IC Markets Forex.com
Forex.com AXITrader
AXITrader