Understanding the forex industry can be a complex endeavor. However, with careful research, it’s possible to grasp its nuances and move toward a profitable picture. One aspect is foreign exchange swaps.
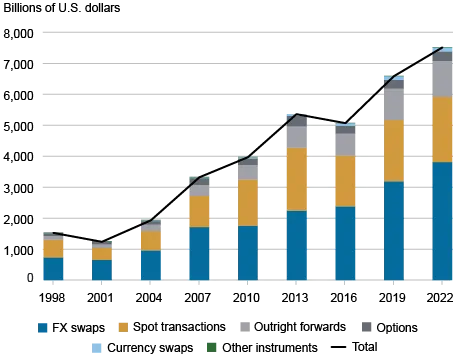
Forex swaps create a huge portion of the forex market globally, which has shown consistent growth over time. In fact, the 2022 Triennial Central Bank Survey by the Bank for International Settlements showed that FX swaps are responsible for 51% of global turnover. That’s an increase since 2019, when the number stood at 49%. I know from experience how a strong understanding of forex swaps can be beneficial for businesses and traders. In this guide, we’ll explore forex swaps in detail, however, it’s a good idea to understand how to read forex charts before we begin.
Fundamentals of Forex Swaps
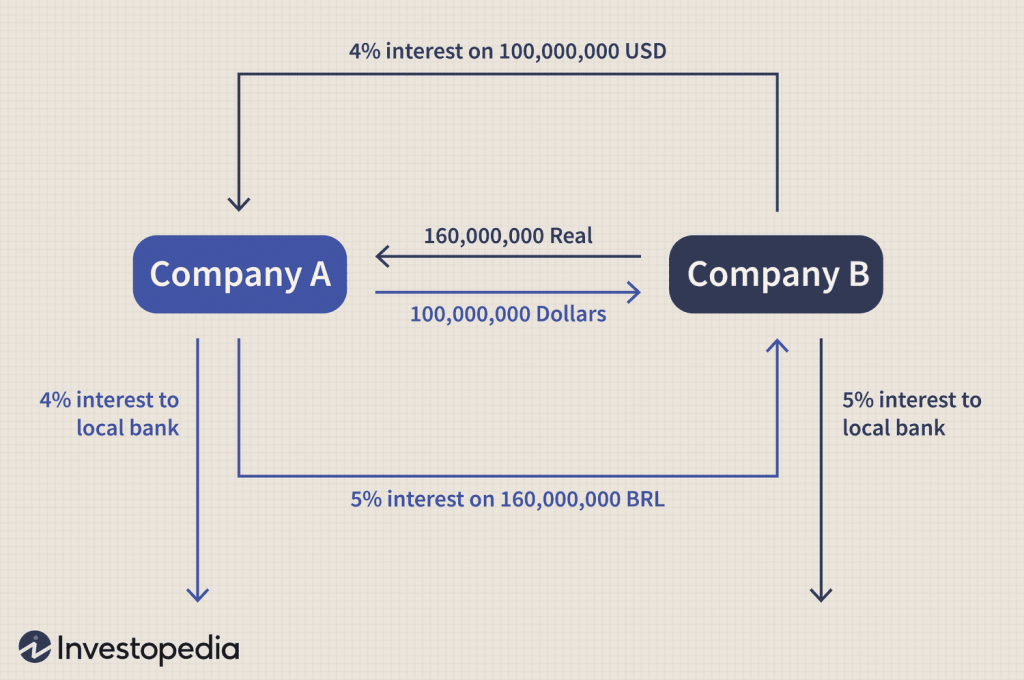
Before we begin, we need to define forex swaps. In essence, forex swaps are a tool used in currency trading. They are an agreement between two parties to exchange currency pairs at a specific date in the future.
For instance, imagine that a large company is expecting payment in euros three months in the future. If the current exchange rate is favorable, they may arrange a forex swap to lock in that rate. They would then sell euros and buy dollars in the spot market, simultaneously agreeing to buy euros and sell dollars in three months’ time. If the rate is less favorable in three months’ time, they’re protected from losses.
Components of a Forex Swap
There are two main parts to any foreign exchange swap: the spot leg and the forward leg.
The spot leg is the currency exchange that takes place at the current market rate. The forward leg is the agreement between the two parties to reverse the transaction at a set date in the future, and at what rate.
The spot leg component meets immediate liquidity needs, whereas the forward leg manages currency risk.
Types of Forex Swaps
Within this, there are a few types of forex swaps and they all have a specific purpose. Spot forward swaps are the most common. In this case, one leg (component) is a spot transaction and the other is a forward transaction. However, there are also forward-forward swaps and that means both legs are forward transactions with different maturity rates.
Market Participants
The FX swap market is dominated by large financial institutions. Within that, banks are the most prominent, along with corporations and institutional investors.
Banks use forex swaps in liquidity management, while also using them to facilitate client transactions. Corporations use FX swaps to manage currency risk and international cash flow. Finally, institutional investors use forex swaps within their investment strategies.
These participants are very active, and the Bank for International Settlements reports that interdealer trading was responsible for 46% of global forex turnover in 2022. This was up from 38% in 2019.
Mechanics and Pricing
In order to use forex swaps, it’s important to understand how they work in practice and how specific rates are calculated.
Simply put, forex swap pricing involves complex calculations based on differences in interest rates. Swap points are a key concept within this, as they determine the cost of a forex swap. The forward rate is calculated from the spot rate and the interest rate differentials. This video helps explain this complicated calculation in more detail.
Swap Points
The swap point is the fundamental part of FX swap pricing. This point represents the difference in interest rates between the two currencies. Calculating this swap point means identifying the spot rate, the interest rates of both currencies, and the time maturity involved.
Swap points can be positive or negative, and this depends on the interest rate differential. Once calculated, traders use the swap point to understand the cost or benefit involved in the currency position. It is a key player in forex swap decision-making.
However, this trading strategy is a relatively short-term one. According to a CFA Institute blog post, more than 90% of forex swaps mature in less than three months.
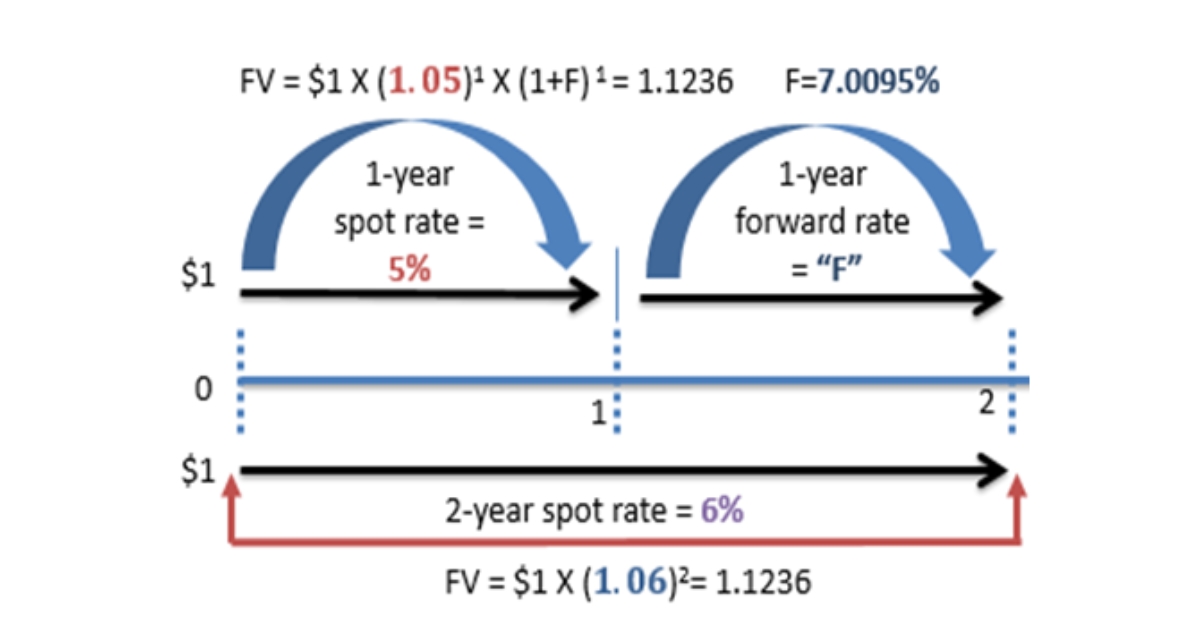
Forward Rate Calculation
Calculating the forward rate in forex swaps takes into account a specific formula using the spot rate and interest rate differential. The forward rate is a vital part of the puzzle as it determines the swap rate in the forward leg of the arrangement.
Let’s say the spot rate for EUR/USD is 1.1000, the 1-year interest rate for EUR is 1%, and for USD is 2%. The forward rate would be calculated as: Forward Rate = Spot Rate * (1 + Interest Rate EUR) / (1 + Interest Rate USD) = 1.1000 * (1.01 / 1.02) ≈ 1.0892. This means that in the forward leg of the swap, 1 EUR would be exchanged for 1.0892 USD.
Valuation and Mark-to-Market
The process doesn’t end once a forex swap has been calculated. The next step is marking to market. This means reassessing the value of the swap based on market conditions in the moment and this is a vital step to assess risk management. A big change in interest rates and spot exchange rates can drastically affect swap valuations, so this step is key in managing such risk.
Regular valuation helps businesses comply with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. However, it’s important to remember that the forex swap world constantly shifts and changes. To demonstrate that, CME Group launched FX Spot+, which looks to give more efficiency and transparency in FX swap trading. This will impact how forex is valued and traded in the future. As a result, it’s vital to stay up to date with these developments, to ensure forex swaps remain viable and profitable.
Swap Curves
Another key element of FX swap pricing is swap curves, which play a key part in pricing and risk management. Swap curves demonstrate the connection between swap rates and maturities for each currency pair. Understanding this concept gives important insights into the market conditions and aids in decision-making.
| Maturity | Swap Points (EUR/USD) | Implied Forward Rate |
| 1 Month | -2.5 | 1.0975 |
| 3 Months | -7.8 | 1.0922 |
| 6 Months | -16.2 | 1.0838 |
| 1 Year | -32.5 | 1.0675 |
Applications and Strategies
The next step in our comprehensive guide to forex swaps is understanding how they’re used and for what purposes. The most common include cash flow management, hedging, and speculative strategies.
However, before we jump in, it’s important to understand how to create and manage a forex trading strategy. Our resource offers some key advice and this will help you add forex swaps into your trading approach.
Hedging with Forex Swaps
One of the most common ways companies use foreign exchange swaps is through hedging. This is a strategy that protects against currency fluctuations. Earlier, I gave an example of a US company expecting a large payment in euros three months later. This company could use a forex swap to set the current exchange rate, therefore using hedging.
Ultimately, forex swaps allow companies to reduce foreign exchange risk without having their capital tied unnecessarily. It provides a flexible tool for matching assets and liabilities in different currencies, and hedging can stabilize cash flow and help with planning.
Cash Flow Management
Forex swaps can also be used to manage cash flows across various currencies. Overall, they allow companies to swap cash in one currency temporarily for another currency they need at that moment. By doing this, they reduce risk, and it’s a particularly useful strategy for large multinational corporations that deal with cash in various currencies.
We can look at an example to illustrate this point. A Japanese company has excess yen but they need dollars to fund a short-term project. They can swap the yen for dollars now, use them for their project, and then swap back to yen once the swap period is over. By doing that, they can meet their needs without converting their yen reserves permanently.
Speculative Strategies
Another reason for an exchange swap is a speculative purpose. This may involve using favorable interest rate differentials between currencies or anticipating exchange rate fluctuations. However, these strategies do come with increased risks due to leverage that can boost both gains and losses.
Carry Trade
Another commonly used strategy is carry trade. This is another speculative strategy that means borrowing a currency with a low interest rate and investing in a currency with a high interest rate. An FX swap can be used to allow traders to roll over their positions, however it’s a risky situation if exchange rates shift unfavorably.
For instance, if a company might borrow yen with a low interest rate and convert to Australian dollars with high interest rates. They would then use the Australian dollars to invest in high-yield assets. The profit will arrive from the interest rate differential but if the yen appreciates by a large amount against the Australian dollar, they will lose out.
Risks and Considerations
All trading strategies have risks involved and forex swaps are no different. It’s important to understand these risks before considering this strategy for yourself. The most common risks are market risk, counterparty risk, and liquidity risk. Let’s explore these in more detail.
Counterparty Risk
Counterparty risk is a significant issue to consider in foreign exchange swaps. In this case, the other party in the swap might not fulfill their side of the deal. For this reason, it’s important to deal with reputable financial institutions only, and in that case, the risk will be low.
The CFA Institute states that the top 25 banks in the US make up more than 80% of forex swap positions. This highlights how to reduce counterparty risk. However, collateral management is another useful way to reduce this risk. This means one or both parties post collateral to cover any potential losses during the exchange swap. However, it does make the transaction more complicated.
Market Risk
Another potential issue is market risk. This is very common in forex swaps because of potential fluctuations in exchange and interest rates. Even companies that regularly use hedging strategies can lose out due to unexpected market ups and downs. This highlights the importance of understanding market dynamics and continuous monitoring.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk means the difficulties in unwinding or rolling over positions during times of market stress. Generally, the forex swap market is liquid, but sometimes this can be less so, and it’s challenging to adjust or exit positions without large fees.
To help in this regard, LMAX Group recently acquired FX HedgePool with the aim to boost liquidity in the institutional FX swap market.
Regulatory Environment
Understanding the regulatory landscape in relation to FX swaps is vital for anyone looking to get involved in this strategy. The regulatory environment has changed a lot over the last few years, mostly aiming to increase transparency and reduce systemic risk.
It’s also true that compliance requirements can sometimes impact the cost and complexity of forex swaps. Additionally, different jurisdictions may have varying approaches.
Global Regulatory Framework
Worldwide regulatory bodies oversee forex swaps to ensure fairness and compliance. In the US, it is the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), in Europe, it is the European Securities and Markets Authority (EMSA).
It’s important to stay up-to-date with regulatory changes. For instance, new UPI rules were implemented by the CFTC in January 2024, which impacted forex swap transactions.
Reporting Requirements
Over the last few years, mandatory reporting requirements have been introduced for foreign exchange swap transactions. While these requirements do vary according to the jurisdiction, they have the same aim: to provide regulators with a clear idea of market activity and risks.
While complying with these requirements can sometimes be complex, it’s an essential aspect.
Clearing and Settlement
Another key trend is the push toward central clearing for FX swaps. This aims to reduce counterparty risk by having a central counterparty between both parties in a transaction. Not all FX transactions need to be centrally cleared but it’s possible that they will be in the future.
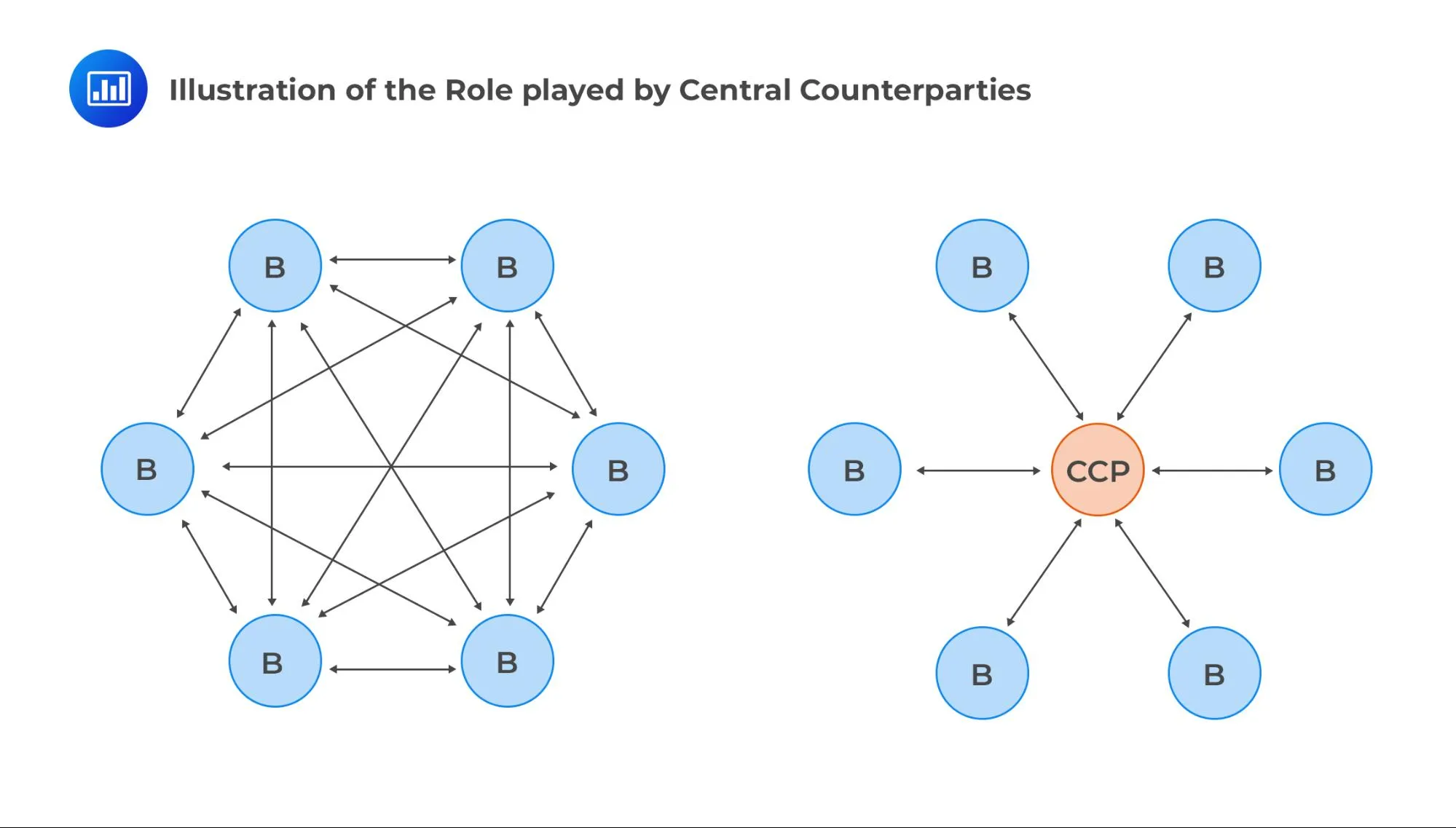
Bilateral vs. Cleared Swaps
Choosing between cleared and bilateral forex swaps requires careful consideration. Cleared swaps reduce counterparty risk and often have better pricing. However, they also have additional costs and complexities. On the other hand, bilateral swaps give more flexibility but may have higher counterparty risks.
Making the decision depends on the risk tolerance and needs of both parties.
| Aspect | Bilateral Swaps | Cleared Swaps |
| Counterparty Risk | Higher | Lower |
| Flexibility | High | Limited |
| Operational Complexity | Lower | Higher |
| Regulatory Oversight | Less stringent | More stringent |
| Cost | Potentially lower | Additional clearing fees |
Technological Advancements
Technology is shaping all areas of our lives and how we trade is no different. In the forex swap market, there are various types of technology that streamline and boost efficiency. Electronic trading platforms and blockchain applications are just two notable mentions, and they’re changing how forex swaps are initiated, arranged, and managed.
Let’s explore these advancements in more detail:
Electronic Trading Platforms
Over the last few years, electronic trading platforms have revolutionized forex swaps. Not only do they make trading faster and more efficient, but they lead to the discovery of better prices. It’s also a lot easier for more people to access the market. Such platforms provide automated execution, real-time pricing, and post-trade processing. Overall, they streamline the trading process.
CME Group’s FX Link platform launched in 2018 and provides a central limit order book for trading electronically. This positive advancement allows traders to execute different trades simultaneously, giving improved price transparency and execution efficiency.
Algorithmic Trading
Another key advancement is algorithmic trading, which has become very common in the foreign exchange swap market. Complex algorithms quickly analyze market data and identify potential opportunities. They also allow for trades to be executed at high speed.
Algorithmic trading can certainly enhance trading efficiency, but they can also be challenging and create more risk, especially during market stress. In this case, a strong risk management strategy is required.
Blockchain and Smart Contracts
Both blockchain technology and smart contracts can change the forex swap market in big ways. Over time, it’s thought they could streamline the settlement process, reduce counterparty risk, and also increase transparency.
These technologies are still in their infancy and widespread adoption is yet to occur, but many industries are exploring them.
Data Analytics and AI
It’s impossible not to mention AI and data analytics, and these are two areas often used in FX swap trading and risk management. Both of these technologies can be used to help analyze large amounts of data and recognize patterns. This leads to better decision-making outcomes. Additionally, both of these technologies are used to improve risk management processes, such as scenario analysis and stress testing.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
It’s clear that the forex swap market is always shifting and changing, and it’s influenced by many different factors. Looking to the future, there are several trends on the horizon, and it’s important to understand them and how they may affect FX swaps.
Market Size and Growth
It’s clear that the foreign exchange swap market is large and it’s showing no signs of slowing down – quite the opposite. According to the 2019 Triennial Central Bank Survey, the annual daily turnover in the forex market was $7.5 trillion in April 2022. This is expected to grow year upon year.
There are many reasons for this rapid growth, including cross-border investments and increased global trade in general. However, it also shows the increased importance of forex in global finance.
Emerging Market Currencies
There are many emerging market currencies to consider in the forex swap market. These include the Chinese yuan, Brazilian real, and Indian rupee, which are all becoming more prominent. This shows the changing dynamics of global trade and the growing economic importance of these countries. Of course, this brings new opportunities to traders, along with challenges.
The Bank for International Settlement states that the Chinese yuan’s share in global FX turnover increased by 7% in 2022. This makes it the fifth most traded currency, compared to 2019 when it was in eighth place.
ESG Considerations
We also need to consider how ESG factors (environmental, social, and governance) influence the forex swap market. More people are considering sustainability and ethical practices in their financial decisions and trading strategies. This has prompted the development of ESG-linked forex products and also influences how traders approach risk management.
Sustainable Finance
Sustainable finance is a buzzword in the foreign exchange swap arena. Green forex swaps are linked to environmentally friendly projects and they are becoming very popular. These allow traders to support sustainable initiatives while also managing their currency risk.

Learning Recap
Understanding forex swaps in greater detail is key to successful trades. We’ve covered the basics to the more advanced concepts, while exploring the possible future trends. Here is a short recap on the most important points:
- Forex swaps are agreements to exchange currency pairs at future dates, combining spot and forward transactions.
- They serve various purposes, including hedging, liquidity management, and speculation.
- The pricing of forex swaps involves concepts like swap points and forward rate calculations.
- Market participants include banks, corporations, institutional investors, and central banks.
- Risks associated with forex swaps include counterparty, market, and liquidity risks.
- The regulatory environment for forex swaps continues to evolve, with a focus on transparency and risk reduction.
- Technological advancements, including electronic platforms and blockchain, are reshaping the forex swap landscape.
- Emerging market currencies and ESG considerations are becoming increasingly important in the forex swap market.
Successful trading requires constant learning, and at TopBrokers, we’re committed to helping all traders continually develop their skills.
For instance, our resource on the Gartley pattern and how to trade with it is extremely useful. In addition, we have a range of comparisons between brokers and other educational resources related to the trading world.

 RoboForex
RoboForex Exness
Exness FxPro
FxPro Alfa-Forex
Alfa-Forex Libertex
Libertex FxGlory
FxGlory XM
XM IC Markets
IC Markets Forex.com
Forex.com AXITrader
AXITrader